Draft Taxonomy Regulation risks undermining Renovation Wave

EU Taxonomy defines what qualifies or not as a ‘green’ investment. The current draft guidelines allow very weak renovations – just 30% energy savings – to meet taxonomy requirements. To ensure a clear signal to investors and make sure the Green Deal delivers its full social, economic, and environmental potential, we urge the Commission to increase the current 30% energy savings requirement to at least 60%.
REDay Exhibition 2019

For Renovate Europe Day 2019, we collected 29 best-practice cases of deep energy renovation from across the EU. These were displayed in an exhibition inside the European Parliament from 7-11 October 2019. You will find the information from the exhibition, as well as further resources on each project and programme, below
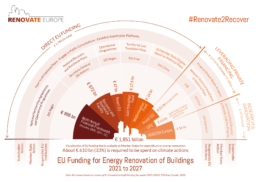
REDay2020 - #Renovate2Recover

“This is YOUR moment,” was the key message from Executive Vice-President Frans Timmermans on 27th October at Renovate Europe Day 2020 (REDay2020). Referring to the National Recovery and Resilience Plans that Member States must submit, Timmermans emphasized widespread support for renovation: “I have never seen such enthusiasm from Member States for any initiative (…) they know that renovation is low-hanging fruit for low emissions and job creation”
Towards EU Member States Economic Recovery: The potential of buildings in delivering jobs and a better quality of life.

Maria Spyraki MEP is the rapporteur for the opinion “Maximising the energy efficiency potential of the EU building stock” on behalf of the European Parliament’s Committee on the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety (ENVI).

The EU has long been considered a frontrunner in the field of climate and environment policy. In that perspective, the European Green Deal, a set of policy initiatives by the European Commission with the overarching aspiration of making Europe climate neutral in 2050, aims for the EU transition to a climate neutral, modern, resource-efficient and competitive economy as well as a fair and prosperous society. The Green Deal is a roadmap which includes complementary steps and initiatives which will nudge the Member States, stakeholders and citizens in coordinating their actions faster and more efficiently.
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the social norms and the usual steps included in the Green Deal. It started as a health crisis, but it has rapidly transformed into an economic one. According to the World Economic Forum, the recession in the Eurozone is assessed at 8.7% for the year 2020. For Greece, the same assessment is 8-9.9%. Until now, the crisis has led to a steep increase in unemployment numbers, a fall in growth-enhancing investment and higher public debt.
Against this background, the Next Generation EU (NGEU) was launched at a European level. This Initiative will enable the European Commission to raise up to €750bn from the financial markets to tackle the effects of the COVID-19 crisis. The entire package has been negotiated with the EU’s next seven-year budget (2021-2027) in mind. It will be worth at least €1,074 billion.

Within the framework of the NGEU, the Recovery and Resilience Facility, which consists of large-scale financial support to both public investments and reforms (notably in green and digital), will support the Member States in their economic recovery while respecting their pledges under the EU Green Deal. To access funding stemming from this Facility, the Member States will have to draft National Recovery and Resilience Plans, which will have to be in line with their National Energy and Climate Plans (NECPs) and European Semester Country recommendations. These Plans present a unique opportunity to make energy renovation of buildings, along with the recyclability of materials (according to the new Circular Economy Action Plan) and other green investments, central to the EU Member States recovery strategies. In fact, the National Recovery and Resilience Plans, if well-designed and ambitious enough will have the potential to prove to be just what is needed to accelerate the EU’s pace towards full decarbonisation while rebooting its economy after the devastating economic downturn. Additional funding could be unlocked by leveraging the Multiannual Financial Framework (MFF) and other instruments stemming from the Recovery Package such as REACT-EU, the Just Transition Fund, InvestEU Fund (managed by the European Investment Bank), national budgets and private sources.
So, after all, this pandemic can be seen as a wake-up call and an opportunity to do things right, as Mr Antonio Guterres (Secretary-General of the United Nations) said. We need “quick wins” to address the needs of the citizens, especially during the first years of the recession. In this regard, if the EU Member States take on the opportunities lying behind the upcoming Renovation Wave Initiative, which is among the European Green Deal’s policy initiatives, they could truly restart the economy with the right foot. Until now, we have had a low rate of energy renovation of building at Member State-level, which has been swinging between 0.4-1.2% per year. In the European Parliament, we set a very ambitious target of 3% yearly, starting from public buildings. According to the recent REC Study, prepared by the BPIE, for every €1 million invested in energy renovation of buildings, an average of 18 jobs is created in the EU. Beyond macro-economic effects, improving the energy performance of buildings would help alleviate energy poverty by reducing the bills of nearly 50 million households affected by it across the EU. Additionally, this will bring healthy and safe living conditions. Moreover, energy upgrades of buildings could boost local economies by creating local jobs, such as experts and service engineers to audit current installations and install new energy-efficient technologies.

In conclusion, money alone will not be enough to restart the EU economy in green and smart away. There is a need to focus on long-term policies and investments to build a more resilient society. That includes a strong focus on the transition to a low-carbon economy, especially by reducing the energy demand of our building stock, to be sure to deliver a better future to the next generations.
Leveraging carbon revenues in the EU Renovation Wave
Background
The European Green Deal calls for a just, clean energy transition and makes a commitment to ‘leave no one behind.’ The state of EU buildings creates a dual challenge for decarbonising the 27 EU economies. First, buildings account for 40% of EU energy demand and 36% of greenhouse gas emissions, with those average figures varying widely from country to country. Second, inefficient homes are the main reason some 50-100 million EU citizens currently live in situations of energy poverty.
Considering that 97% of EU buildings need some level of energy renovation, some estimates put the cost at €300 billion per year for the next 30 years – €1 billion per day, every day until 2050. But counting just the costs misses the more important point: according to the International Energy Agency, aggressively implementing energy efficiency on a global scale could deliver benefits of €500 billion annually.
The Renovate Europe Campaign is pleased to see the call for a Renovation Wave within the EU Green Deal – and is actively engaged in shaping its strategy. Knowing that such an effort must be undertaken strategically, we’ve launched this podcast series to give voice to a range of experts to explore topics such as who needs to take action — when, where, why and how — in order to optimise efficiency gains and returns on investment. As sustaining a renovation wave will require effective policy and large-scale practical action, we will investigate examples of early movers who can show promising results.
For this podcast series, the Renovate Europe Campaign is collaborating with The Energy Action Project (EnAct), acknowledging their important reporting on energy poverty the EU through the COLD@HOME website.
Podcast 1: Leveraging carbon revenues in the EU Renovation Wave

The Renovate Europe Campaign invites Louise Sunderland of the Regulatory Assistance Project (RAP) to talk about her recent research, which shows that using carbon revenues to fix the homes of low-income families delivers better returns than existing stop-gap measure to reduce the impacts of energy poverty. Louise also brings the perspective of volunteering at a community energy cooperative in South London that provides services to low-income households. With host Marilyn Smith of The Energy Action Project (EnAct), this podcast digs into the reality that people spend 90% of their time indoors and homes make up 75% of the EU building stock. The renovate challenge is exacerbated by huge variety in housing types and the need for large-scale investment, delivered in relatively small sums.
Speaker: Louise Sunderland, The Regulatory Assistance Project (RAP)
Host: Marylin Smith, the Energy Action Project (EnAct)
Listen here: https://soundcloud.com/user-443004419/leveraging-carbon-revenues-in-the-eu-energy-renovation-wave/s-1nYVltEHqtL